In Polar Coordinates The Center Of The Coordinate System Is Called The
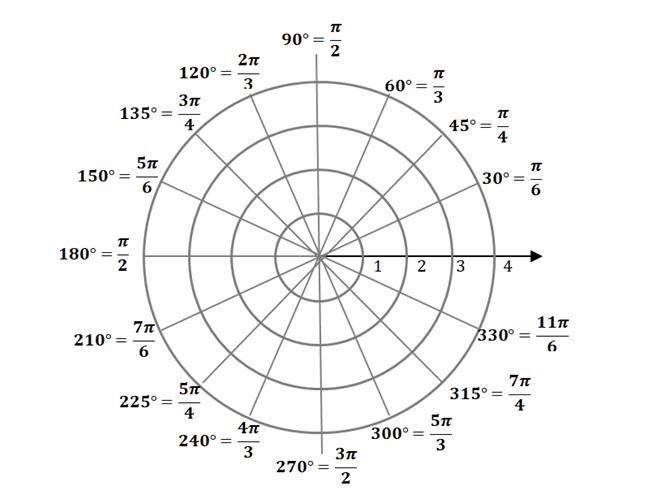
In polar coordinates the center of the coordinate system is called the. Universal Transverse Mercator is a projected coordinate system which is a type of plane rectangular coordinate system also called Cartesian coordinate system. More rigorously the coordinate system used is one in which the surfaces r constant are everywhere perpendicular to. Polar grid with different angles as shown below.
In the rectangular coordinate system the definite integral provides a way to calculate the area under a curve. Equal in rank or importance. Application of Coordinate Systems 5.
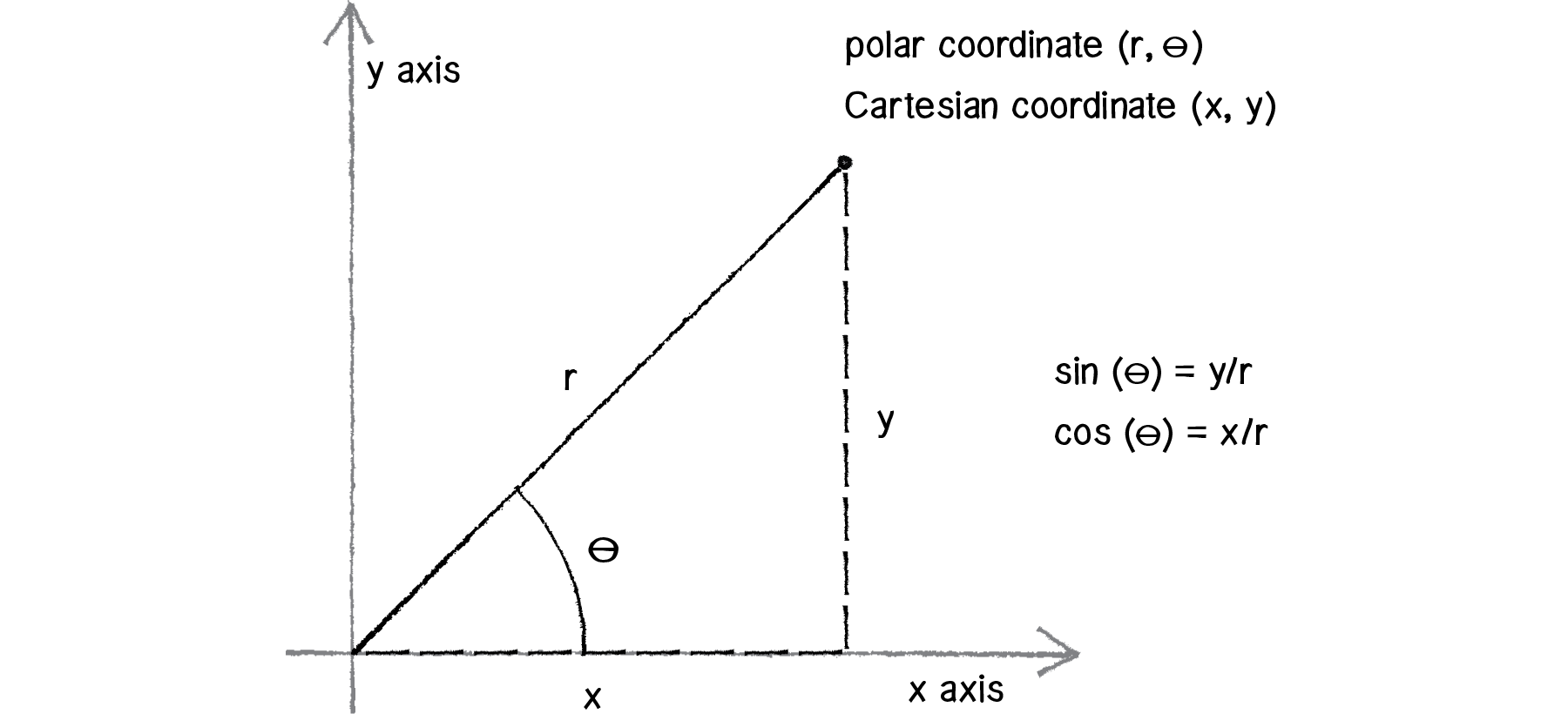
We will derive formulas to convert between polar and Cartesian coordinate systems. In mathbbR2 the equation x 3 tells us to graph all the points that are in the form left 3y right. These types of system are used to represent the polar coordinates of a point in three-dimensions such that the points can be written in the form of.
For example StdDrawsetCanvasSize800 800 sets the canvas size to be 800-by-800 pixels. The obvious and most natural system is spherical polar coordinates λ ϕ r where λ is longitude ϕ is latitude and r is radial distance from the center of the earth. R tanθ 102 Slopes in r pola tes coordina When we describe a curve using polar coordinates it is still a curve in the x-y plane.
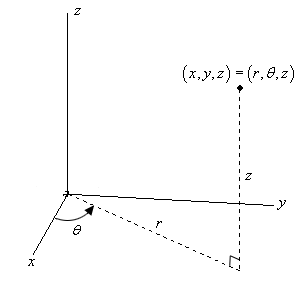
In this section we will introduce polar coordinates an alternative coordinate system to the normal CartesianRectangular coordinate system. Starting with polar coordinates we can follow this same process to create a new three-dimensional coordinate system called the cylindrical coordinate system. The given equation in polar coordinates.
For other coordinate systems the coordinates curves may be general curves. Write a g-code program that feeds the cutter around a 1 inch by 1 inch rectangle whose center is at 1 1. Use absolute coordinates gcode G90.
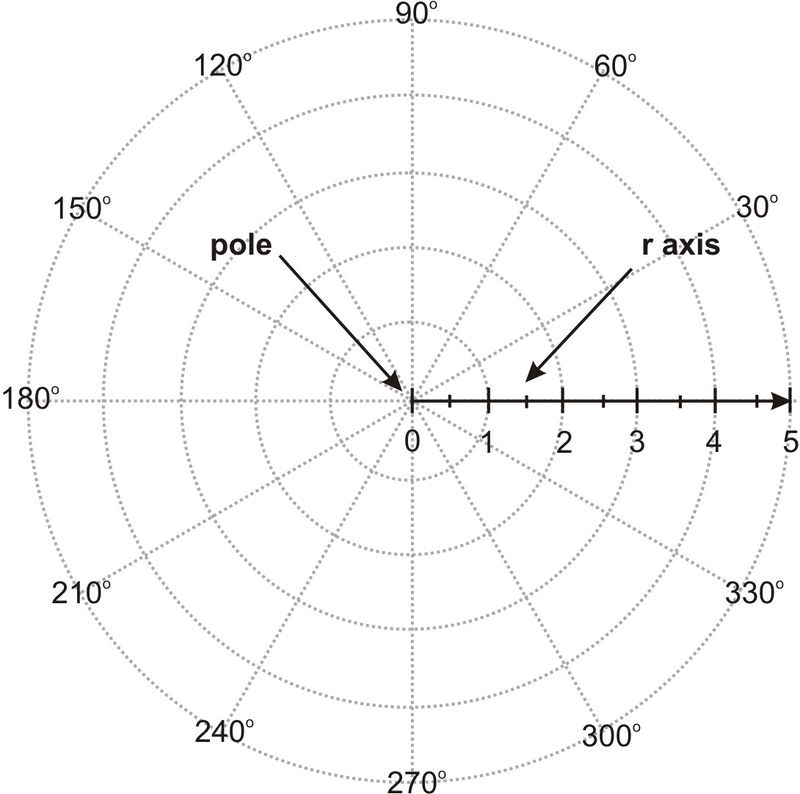
For example the coordinate curves in polar coordinates obtained by holding r constant are the circles with center at the origin. The innermost circle shown in Figure 728 contains all points a distance of 1 unit from the pole and is represented by the equation r 1.
Within each zone a local coordinate system is defined in which the X-origin is located 500000 m west of the central meridian and the Y-origin is the south pole or the equator depending on the hemisphere.
We will derive formulas to convert between polar and Cartesian coordinate systems. Equations for lines in this system will have both the x and y variable. Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinate System. Use absolute coordinates gcode G90. Learn more on polar coordinates here. In particular if we have a function y f x y f x defined from x a x a to x b x b where f x 0 f x 0 on this interval the area between the curve and the x -axis is given by A a b f x d x. In the two. In mathbbR2 the equation x 3 tells us to graph all the points that are in the form left 3y right. We will derive formulas to convert between polar and Cartesian coordinate systems.
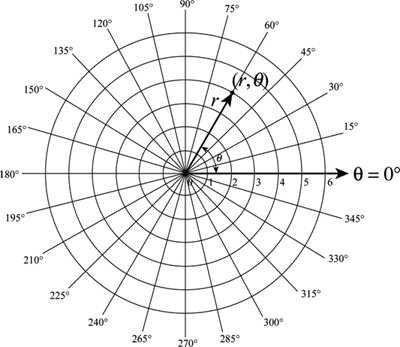
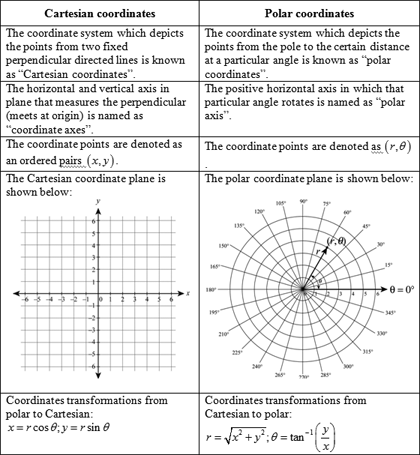
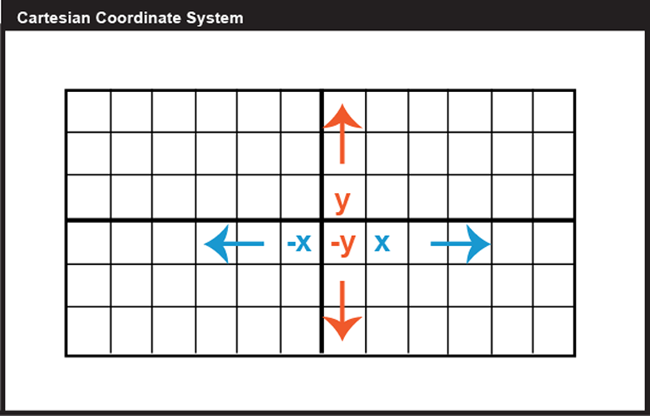
The Cartesian coordinate system uses a horizontal axis that is called the x-axis and a vertical axis called the y-axis. The reference point analogous to the origin of a Cartesian coordinate system is called the pole and the ray from the pole in the reference direction is the polar axis. This type of coordinate reference system is often referred to as a geographic coordinate system. In mathbbR we have a single coordinate system and so x 3 is a point in a 1-D coordinate system. The UCS defines. Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinate System. We will also look at many of the standard polar graphs as well as circles and some equations of lines in terms of polar coordinates.






























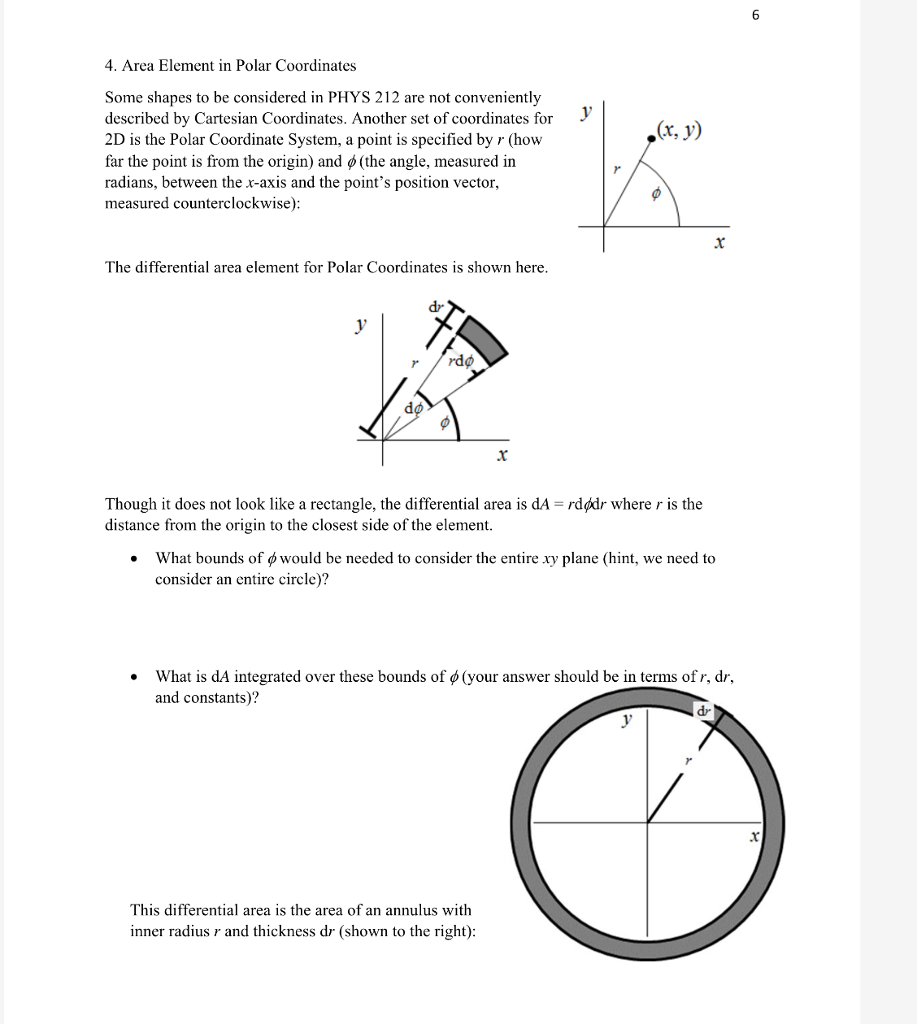
Post a Comment for "In Polar Coordinates The Center Of The Coordinate System Is Called The"