Dry Eye Disease Pathophysiology Classification And Diagnosis
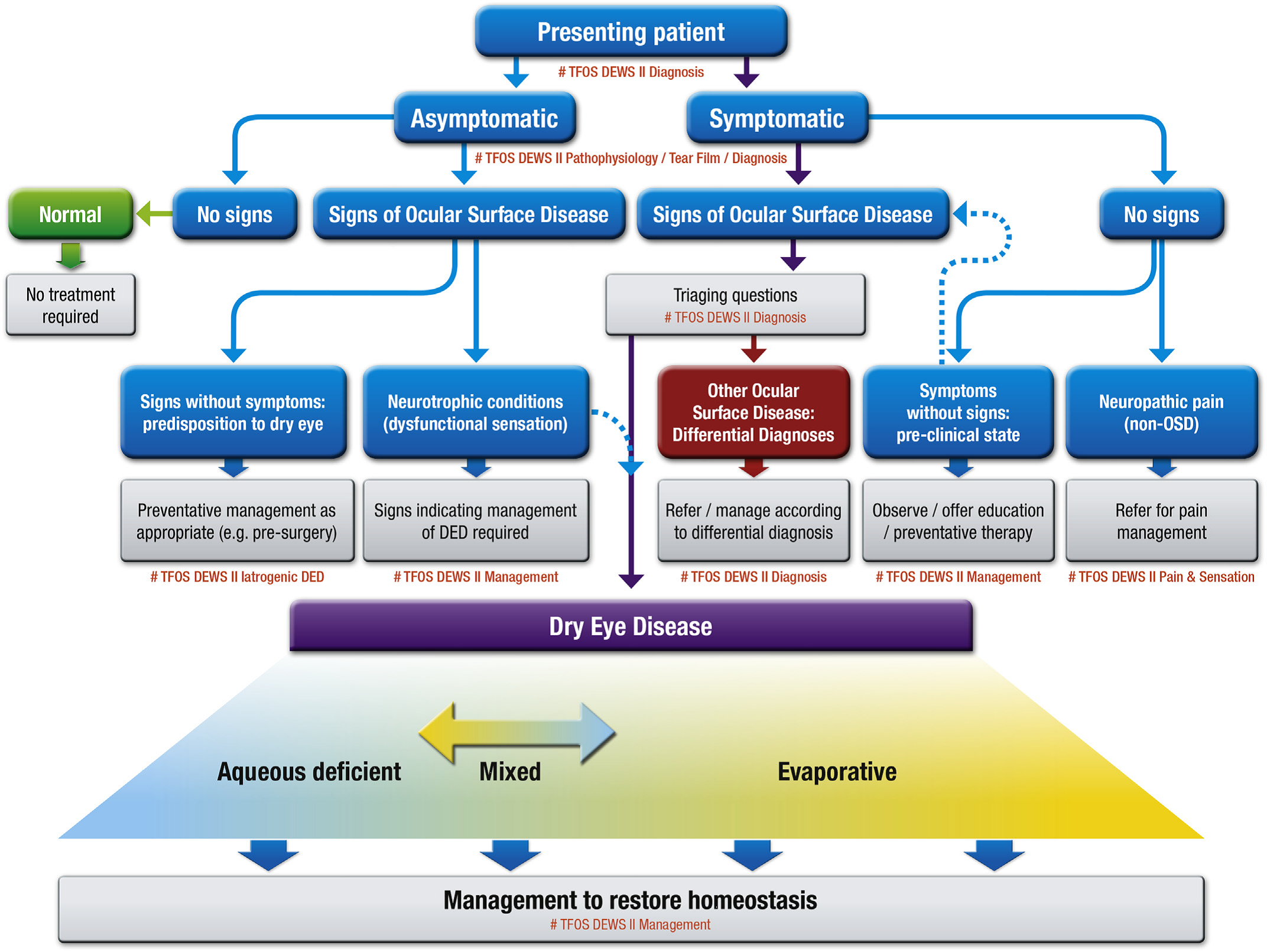
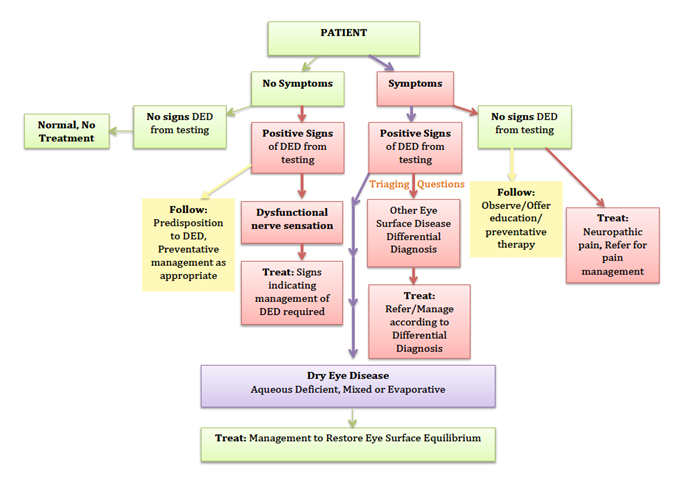
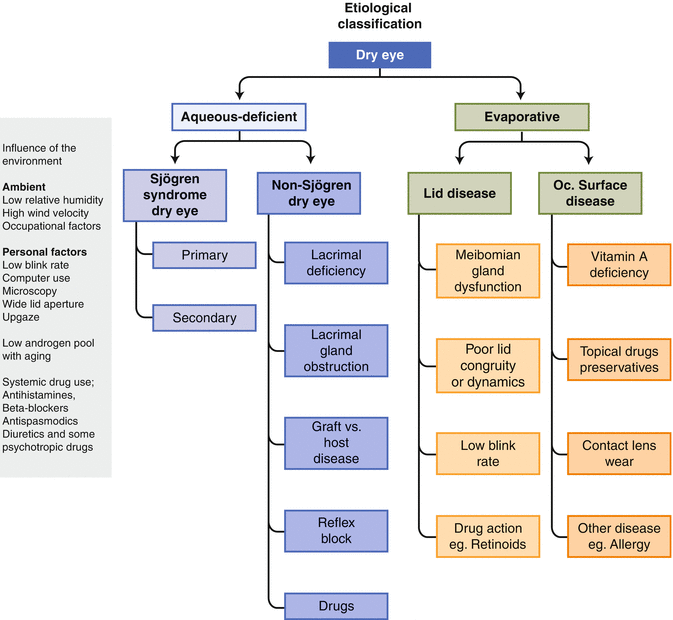
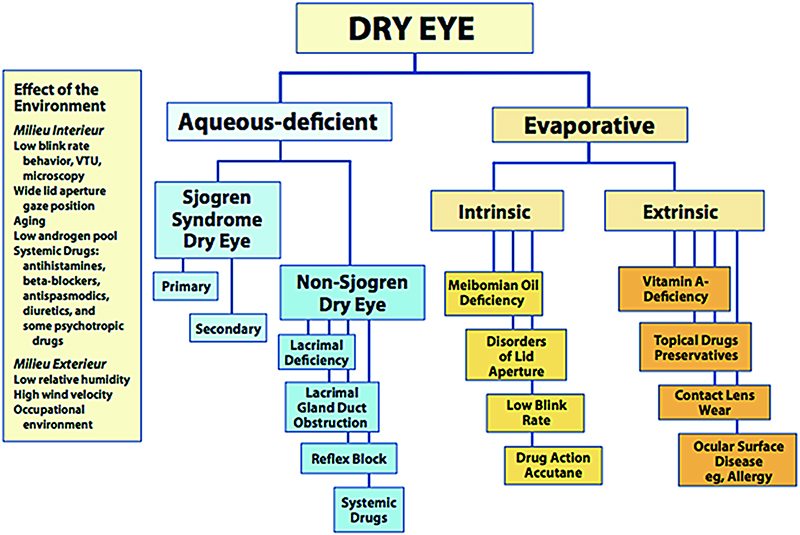
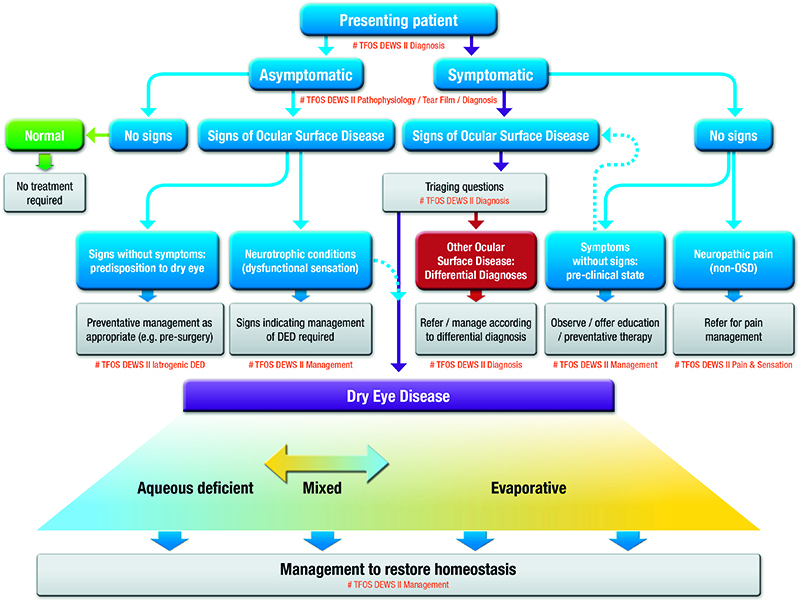
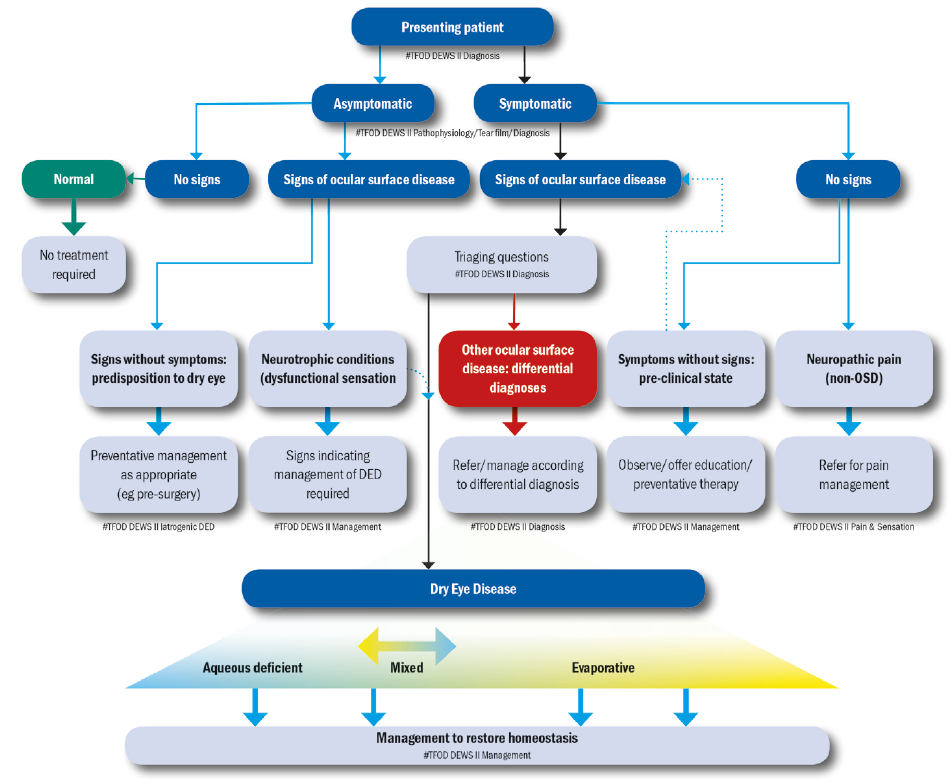
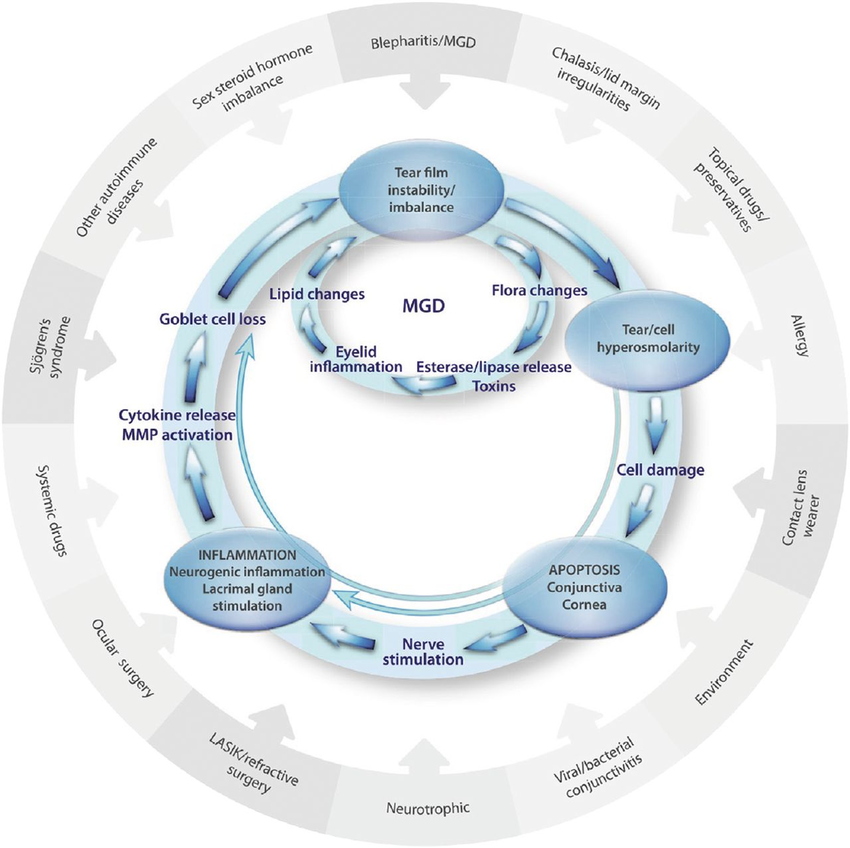
Dry eye disease pathophysiology classification and diagnosis. Dry eye disease is subdivided into two forms aqueous-deficient tear deficiency and hyperevaporative increased evaporation. Severe complications of dry eye disease are rare and are observed in the context of primary or secondary Sjögrens syndrome graft-versus-host disease ichthyosis StevensJohnson syndrome and. Tear film instability and hyperosmolarity ocular surface inflammation and damage and neurosensory abnormalities play etiological roles 1.
1 2 identified the two primary categories of dry eye as tear deficient and evaporative and proposed in sub-classification a range of intrinsic and extrinsic etiological factors believed to contribute to dry eye development within these categories. Dry eye classification schemes serve to guide diagnosis and ultimately improve patient care through appropriate treatment. Dry eye is a multifactorial disease of the ocular surface characterized by a loss of homeostasis of the tear film and accompanied by ocular symptoms in which tear film instability and hyperosmolarity ocular surface inflammation and damage and neurosensory abnormalities play etiological roles 2.
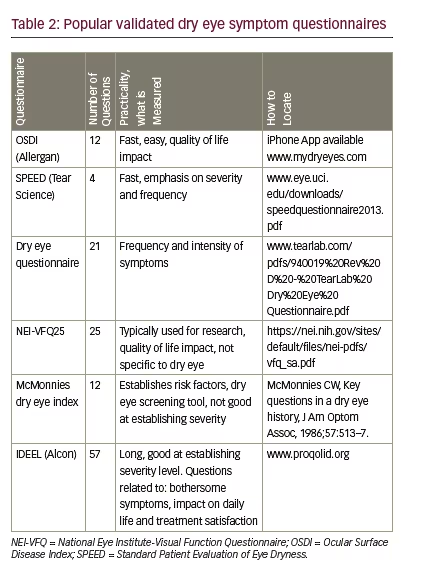
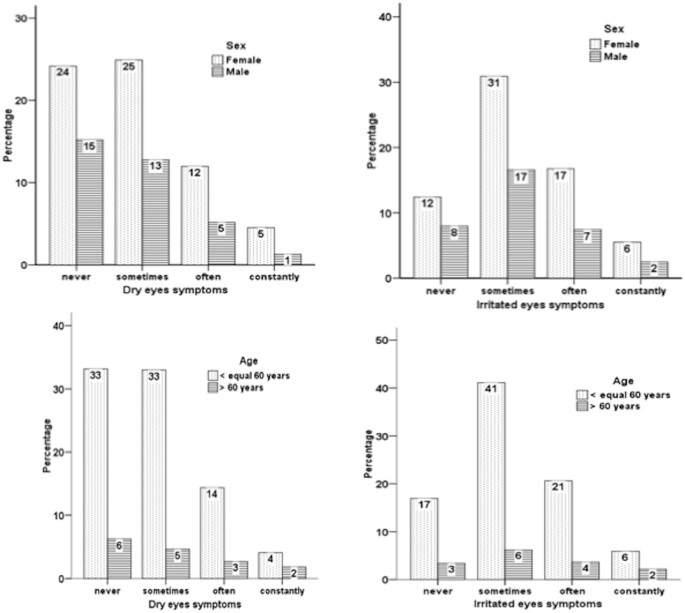
Dry eye impairs functional vision especially in reading at the computer or when driving 9 10 e10 e11. This article discusses the normal anatomy and physiology of the lacrimal functional unit and. The most commonly employed questionnaire is the Ocular Surface Disease Index OSDI which assesses the dry eye-related symptoms eg grittiness pain visual disturbance etc exacerbating factors and impact on daily functioning.
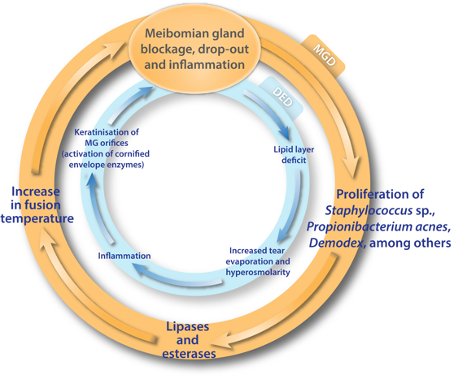
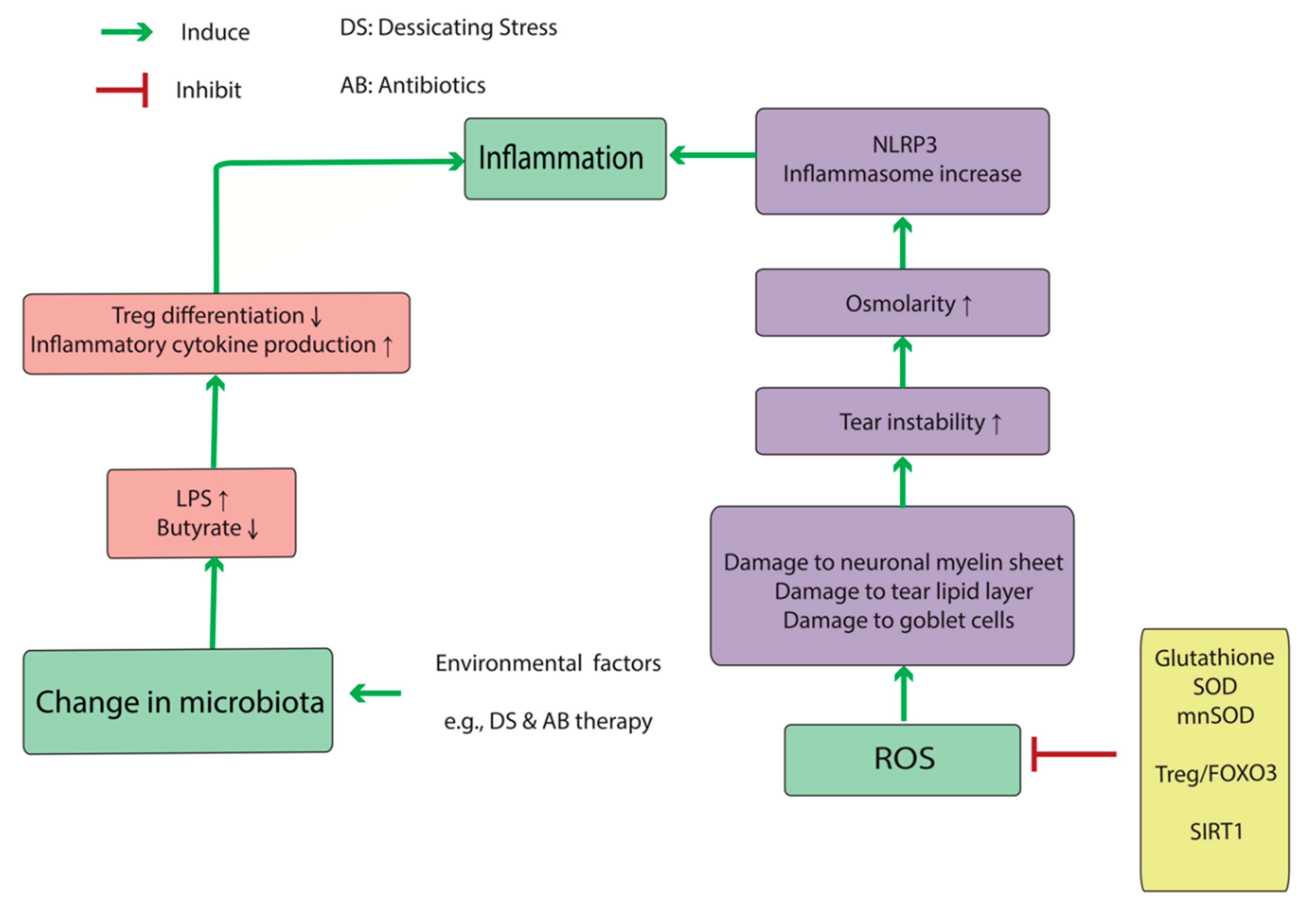
This article discusses the normal anatomy and. Clinical and laboratory studies performed over the past few decades have discovered that dry eye is a chronic inflammatory disease that can be initiated by numerous extrinsic or intrinsic factors that promote an unstable and hyperosmolar tear film. Other ocular surface disease differential diagnoses.
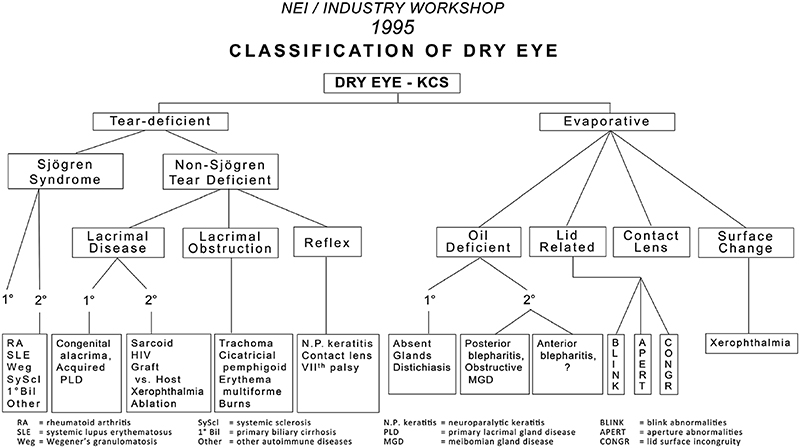
The NEIIndustry Report Fig. Wolffsohn JS Arita R Chalmers R et al. Although recent research has made progress in elucidating DED pathophysiology currently there are no uniform diagnostic criteria.
Dry eye disease is defined as a multifactorial disease of the tears and ocular surface that results in symptoms of discomfort visual disturbance and tear film instability with potential. TFOS DEWS II diagnostic methodology report. Dry eye disease DED is a multifactorial disease of the ocular surface with loss of homeostasis of the tear film and ocular symptoms.
1 Tear instability is accompanied by. Contact lens wear may result in decreased corneal sensitivity with reflex sensory block leading to aqueous.
Dry eye disease DED is a multifactorial disorder of the tear film and ocular surface that results in eye discomfort visual disturbance and often ocular surface damage.
These changes in tear composition in some cases combined with systemic factors lead to an. This article discusses the normal anatomy and physiology of the lacrimal functional unit and. Dry eye disease DED is a multifactorial disease of the ocular surface with loss of homeostasis of the tear film and ocular symptoms. The TFOS DEWS II Definition and Classification subcommittee redefines dry eye as a multifactorial disease of the ocular surface characterised by the loss of homeostasis and accompanied by ocular symptoms in which tear film instability hyperosmolarity inflammation and ocular surface damage and neurosensory abnormalities play etiological roles 3. Although recent research has made progress in elucidating DED pathophysiology currently there are no uniform diagnostic criteria. Other ocular surface disease differential diagnoses. Refers to conditions that may mimic or masquerade as DED eg lagophthalmos inability to fully close the eyelids leading to DED. Contact lens wear may result in decreased corneal sensitivity with reflex sensory block leading to aqueous. Although recent research has made progress in elucidating DED pathophysiology currently there are no uniform diagnostic criteria.
Severe complications of dry eye disease are rare and are observed in the context of primary or secondary Sjögrens syndrome graft-versus-host disease ichthyosis StevensJohnson syndrome and. Dry eye disease DED is a multifactorial disorder of the tear film and ocular surface that results in eye discomfort visual disturbance and often ocular surface damage. Contact lens wear may result in decreased corneal sensitivity with reflex sensory block leading to aqueous. Discover and save your own Pins on Pinterest. 1 Tear instability is accompanied by. Although recent research has made progress in elucidating DED pathophysiology currently there are no uniform diagnostic criteria. This article discusses the normal anatomy and physiology of the lacrimal functional unit and.


























.jpg)
Post a Comment for "Dry Eye Disease Pathophysiology Classification And Diagnosis"