Why Is Huntington's Disease Still In The Population
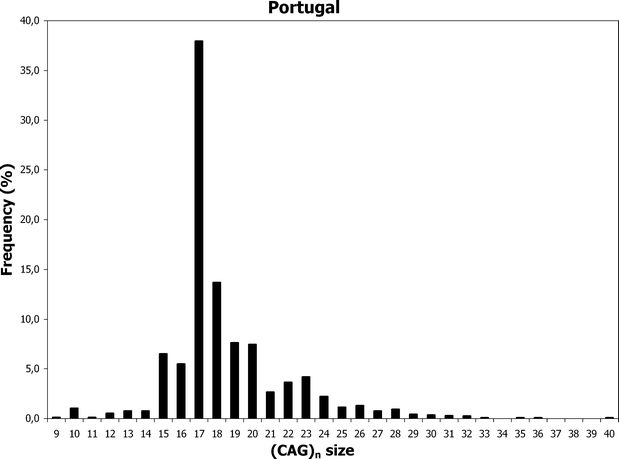
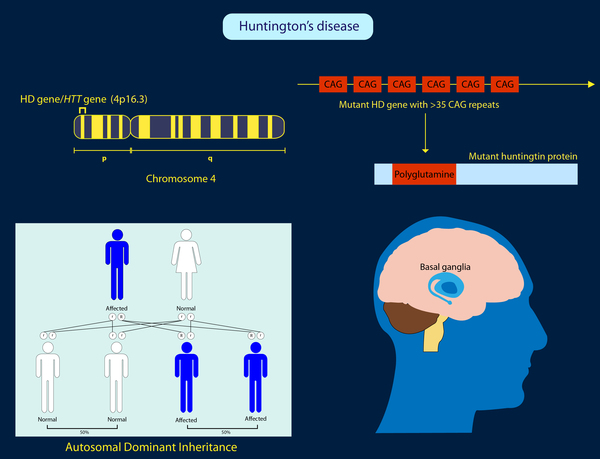
Why is huntington's disease still in the population. Age at onset of diagnostic signs is partly determined by the length of the CAG repeat. Mutation of either of a persons HTT alleles causes the disease. Huntington disease HD affects both men and women of all ethnic groups.
Huntingtons is an incurable and fatal hereditary disease which causes the sufferer to lose control of their muscles. The origin of the gene for the disorder in this population group has been traced over 14 generations from the present time to the days of the first free burghers at the Cape of Good Hope. The direction of selection changes as the environment changes what was advantageous or neutral ten generations ago may be deleterious today.
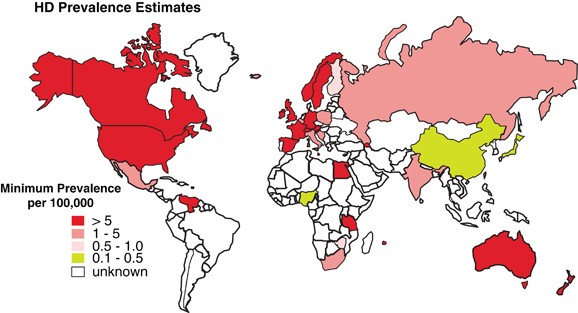
It is caused by the deterioration of various brain regions including the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia. A few isolated populations of western European origin have an unusually high prevalence of HD that appears to. Background and purpose The prevalence of Huntingtons disease HD in the UK is uncertain.
It is not inherited according to sex but by the length of the repeated section of the gene hence its severity can be influenced by the sex of. 1 In general it affects about 3 to 7 per 100000 people of western European descent. The differing functions of these proteins are the cause of pathological changes which in turn cause the disease symptoms.
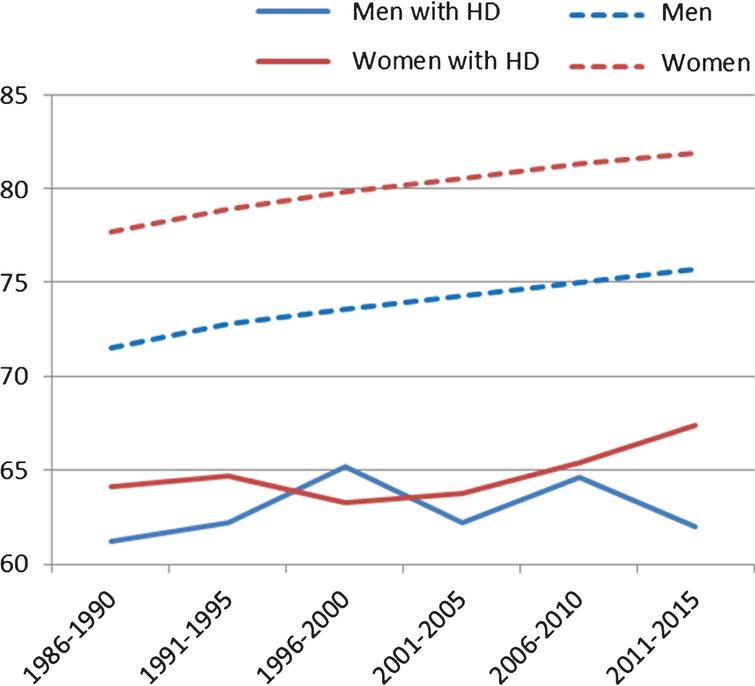
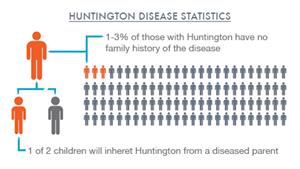
Methods The electronic medical records of patients aged 21. Huntingtons disease HD is an inherited neurological illness causing involuntary movements severe emotional disturbance and cognitive decline. The diagram at left shows how the Huntingtons allele is passed down.
George Huntington April 9 1850 March 3 1916 was an American physician from Long Island New York who contributed the clinical description of the disease that bears his name Huntingtons disease. The Huntingtons disease mutation is genetically dominant and almost fully penetrant. 10 to 15 Irish people in every 100000 will inherit this disease.
63 filas Huntington disease HD is caused by a change mutation in the HTT gene. Recently it has been suggested that the prevalence may be substantially greater than previously reported.
The differing functions of these proteins are the cause of pathological changes which in turn cause the disease symptoms.
It develops into serious problems with swallowing and many patients die from. The differing functions of these proteins are the cause of pathological changes which in turn cause the disease symptoms. Huntingtons chorea is prevalent among the Afrikaner population of South Africa. A few isolated populations of western European origin have an unusually high prevalence of HD that appears to. Age at onset of diagnostic signs is partly determined by the length of the CAG repeat. Huntingtons is an incurable and fatal hereditary disease which causes the sufferer to lose control of their muscles. Huntingtons disease affects around 510 people in 100000 throughout developed countries. This study was undertaken to estimate the overall UK prevalence in adults diagnosed with HD using data from primary care. Mutation of either of a persons HTT alleles causes the disease.
Research on the evolutionary genetics of this disease suggests that there are two main reasons for the persistence of Huntingtons in human populations. Research on the evolutionary genetics of this disease suggests that there are two main reasons for the persistence of Huntingtons in human populations. This results in uncontrollable body movements and stiffening of limbs. In addition 35000 people exhibit some symptoms and 75000 people carry the abnormal gene that will cause them to develop the disease. On Choreawas first published in the. Huntingtons disease affects around 510 people in 100000 throughout developed countries. The differing functions of these proteins are the cause of pathological changes which in turn cause the disease symptoms.
























Post a Comment for "Why Is Huntington's Disease Still In The Population"